Nowadays, cybersecurity is largely an exercise in risk management. As a business, you have to determine which IT risks you can and are willing to accept, as well as what it will cost your business to maintain that level of risk. The digital revolution (accelerated by COVID-19) has increased cyber risks. Moreover, hackers have access to new technologies, exposing your business to more cyber attacks than ever. All this affects your bottom line.
International research agencies regularly study the cybersecurity landscape. But their statistics do not always reflect the situation for businesses in Belgium and the Netherlands. Which is why Proximus, in partnership with Proximus SpearIT, Davinsi Labs and Telindus Nederland, organized its own research among its customers.
How companies
manage
cybersecurity


Methodology
Research report
Secure your business in 4 easy steps
Cybersecurity lexicon

of the respondents were confronted with a cyber incident in 2020
By this we mean any malicious event or action that threatens the reliability, integrity and/or availability of the information systems of a business (the receipt of phishing e-mail, data breaches, unauthorized access, etc. with or without consequences or damage).
50%
The 7 main conclusions of the survey
Every business – big or small – is a potential target

Phishing is the most common attack

An incident is sometimes overlooked

The consequences of an incident are often severe

50% of organizations have no active cybersecurity strategy

Shortage of IT support

The three cybersecurity priorities for 2021



Every organization – big or small – is a potential target
Smaller businesses often think – wrongly – that their data or business is not sufficiently interesting to cybercriminals. SMEs have just as interesting and sensitive data, such as information on customers or companies, intellectual property rights, etc. These data are first and foremost of vital importance to the business itself.
And a data leak or cyber attack is all it takes to damage the relationship of trust with customers, partners or suppliers.
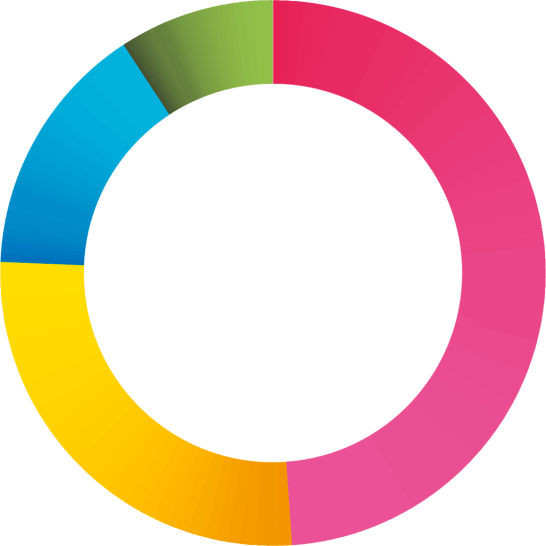
1 in 2 respondents were confronted with a cyber incident in 2020.*
By this we mean any malicious event or action that threatens the reliability, integrity and/or availability of the information systems of a business (the receipt of phishing e-mail, data breaches, unauthorized access, etc. with or without consequences or damage).
54%
34%
12%
54% experienced an incident

34% experienced no incident

12% don’t know

> 2.000
employees
100 – 250 employees
250 – 2.000
employees
< 100
employees
Cyber incidents in small-to-large businesses
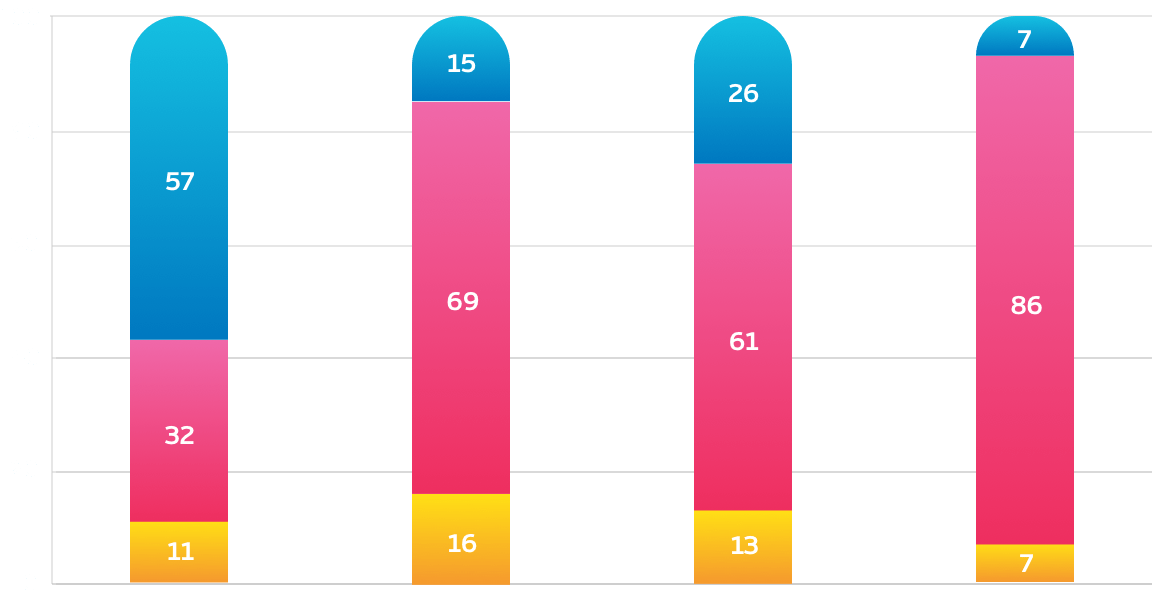
don’t know

had an incident

had no incident

Conclusion
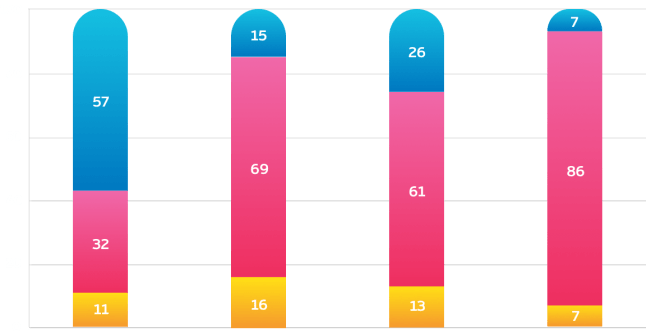
57%
of the businesses with fewer than 100 personnel stated that they had not experienced an incident.
From our 2019 survey it appears that 19% of SMEs (the Netherlands: mkb) were the victim of a cyber incident.
That figure rose in 2020 by 23%, meaning that 42% were the victim of a cyber incident.
*An SME is a company with less than 250 employees. Companies of <100 and 100 - 250 employees fit within this category.
86%
of the businesses with more than 2,000 employees did encounter one or more incidents.
12%
of the businesses surveyed don’t know whether or not they went without incident.

19%
42%
01. Targets
02. Phishing
03. Overlooked incidents
04. The consequences
05. Strategy
06. Shortage of IT support
07. Priorities 2021



Phishing is the most common attack
During the lockdown hackers launched 19% more phishing attacks than ever before. They tried to profit from poorly secured home workstations to steal data or spread malware.
75% of the attacks come from outside the business
3 out of 4 respondents had experienced an incident that came from outside the business, while 1 in 5 was confronted with insider threats.
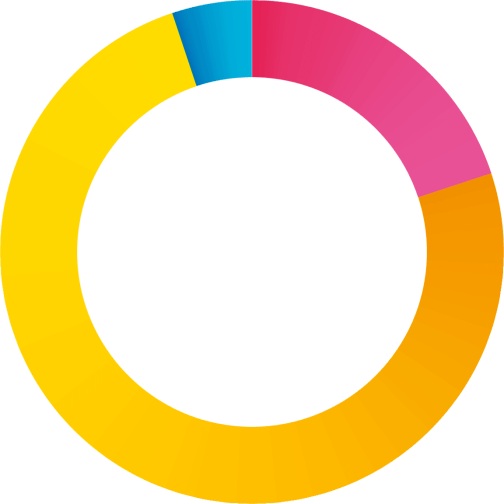
75%
20%
5%
75% External

20% Internal (insider threat)

5% I don’t know

Top 3 cyber incidents in 2020
1. Phishing: 35%
2. Malware: 16%, of which 52% were a virus and 33% ransomware
3. Spear-phising: 16%
01. Targets
02. Phishing
03. Overlooked incidents
04. The consequences
05. Strategy
06. Shortage of IT support
07. Priorities 2021



An incident is sometimes overlooked
For 7 out of 10 respondents, the incident was discovered internally, while 15% were alerted by a third party. An incident cannot always be identified instantly. It demands continuous monitoring and system analysis.
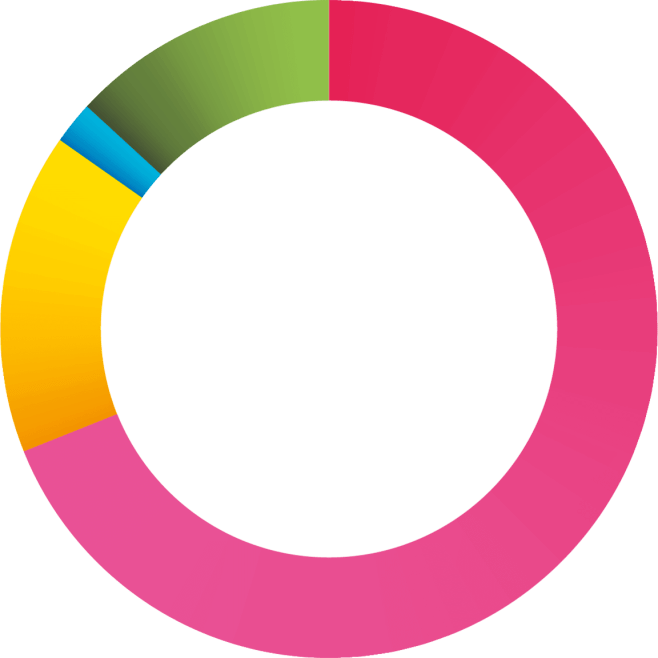
16%
69%
13%
2%
Discovered internally: 69%

Flagged up by third party: 16%

I don’t know: 2%

Other: 13%

01. Targets
02. Phishing
03. Overlooked incidents
04. The consequences
05. Strategy
06. Shortage of IT support
07. Priorities 2021



The consequences of an incident are often severe
Take note: 92% of the businesses that had already experienced a cyber incident are concerned to very concerned about being a victim a second time. Of those businesses that hadn’t yet been attacked, 18% indicated not being concerned at all.
In 9% of cases the incident was such that employees could no longer work.
technical unemployment
Fortunately, in 85% of the incidents no data was lost. However, this was the case in 4% of the incidents. Remarkably – and worryingly – 11% of the affected businesses do not know whether or not they lost data.
loss of business data
actual cost
According to insurance provider Hiscox, Belgian businesses wrongly estimate the costs of cyber incidents. According to businesses, one hacking incident costs 9,000 euros, while in reality that sum can rise to an average of 136,000 euros. A small Belgian manufacturing business with about 500,000 euro annual turnover sometimes loses up to 133,000 as a result of a cyber attack. It is mainly the stoppage of IT followed by planning and production that costs this kind of business handfuls of money.
In our survey many respondents found it difficult to express the costs linked to an incident in terms of percentage of annual turnover. Incidents were discovered in time, so there were no financial consequences for some. While others were faced with the cost of shutting down vulnerabilities and making employees extra aware of cyberthreats.
After an incident, 94% of businesses had the situation under control again within 4 weeks.
Nonetheless, 1 in 20 businesses didn’t have the situation under control after 6 months, which definitely has a huge impact on an organization. In a study by insurance broker Van Breda, in 38% of cases a cyber attack led to a network disruption or business stoppage.
business standstill
Less than a week: 77%

Between 1 and 4 weeks: 15%

Between 3 and 6 months: 2%

Longer than 6 months: 2%

The problem is still not resolved: 2%

I don’t know: 2%


2%
2%
77%
15%
2%
2%
Time out period elapsed before situation was back under control:
01. Targets
02. Phishing
03. Overlooked incidents
04. The consequences
05. Strategy
06. Shortage of IT support
07. Priorities 2021



50% of the organizations have no active cybersecurity strategy
1 in 2 businesses in Belgium and the Netherlands has no active cybersecurity strategy or doesn’t know if they have one.
1. Information security
2. Threat prevention
3. Compliance with regulations
3 major motivations for the implementation of cybersecurity measures
3 major obstacles to the implementation of cybersecurity measures
Cybersecurity is a huge cost for businesses and is rarely if ever included in the budget. In many organizations there is still the perception that cybersecurity means huge costs and little to no ROI.
1. Financial
2. Business culture
If a strategy is not supported by management, then employees are not aware of the importance of cybersecurity and no one cares about it.
The IT environment – often in small businesses – is barely or never monitored. Lack of knowledge, capacity and/or personnel is the cause of this.
3. Resources
01. Targets
02. Phishing
03. Overlooked incidents
04. The consequences
05. Strategy
06. Shortage of IT support
07. Priorities 2021



Shortage of IT support
Almost 4 in 10 respondents admit to having a shortage of specialist people in the IT department. Of those businesses with more than 2,000 employees, 43% reported a shortage of cybersecurity employees.
22% of respondents said they had no cybersecurity employees at all. Of the businesses with fewer than 100 employees, 40% had no cybersecurity team.
Number of cybersecurity employees in the IT department
Who manages and monitors the cybersecurity infrastructure?
01. Targets
02. Phishing
03. Overlooked incidents
04. The consequences
05. Strategy
06. Shortage of IT support
07. Priorities 2021



30%
31%
6%
7%
26%
Cybersecurity priorities for 2021
The study shows that many businesses are still suffering from a shortage of IT support. In addition, there are also businesses that have no strategy or are still developing one. 1 in 4 businesses do not give cybersecurity awareness training to their employees.
Our respondents know that they can and ought to do better. The three top cybersecurity priorities for 2021 are:
1. raising awareness among and training of employees
2. investing in technology
3. developing a cybersecurity strategy
Organizing small activities a few times a year, like a poster campaign or a stand in a central space in the building, can have a much bigger impact. Cybercrime is evolving at breakneck speed, which is why it is important to devote constant attention to the training of your personnel. With (online) mini-training sessions, your employees will constantly be aware of your business security approach.
01. Targets
02. Phishing
03. Overlooked incidents
04. The consequences
05. Strategy
06. Shortage of IT support
07. Priorities 2021
The cybersecurity landscape is a constantly moving picture. It is best to prepare your organization for protecting new technologies and possible cyber incidents.
The 13 cybersecurity trends and risks of 2021
Discover the Proximus 360°approach to making your organization secure. Pick and choose what you want: from total outsourcing to specific cybersecurity services.
Secure your business in 4 easy steps

Nowadays, cybersecurity is largely an exercise in risk management. As a business, you have to determine which IT risks you can and are willing to accept, as well as what it will cost your business to maintain that level of risk. The digital revolution (accelerated by COVID-19) has increased cyber risks. Moreover, hackers have access to new technologies, exposing your business to more cyber attacks than ever. All this affects your bottom line.
International research agencies regularly study the cybersecurity landscape. But their statistics do not always reflect the situation for businesses in Belgium and the Netherlands. Which is why Proximus, in partnership with Proximus SpearIT, Davinsi Labs and Telindus Nederland, organized its own research among its customers.
How companies
cybersecurity
manage


50%
By this we mean any malicious event or action that threatens the reliability, integrity and/or availability of the information systems of a business (the receipt of phishing e-mail, data breaches, unauthorized access, etc. with or without consequences or damage).
of the respondents were confronted with a cyber incident in 2020
Every business – big or small – is a potential target

Phishing is the most common attack

An incident is sometimes overlooked

The consequences of an incident are often severe

50% of organizations have no active cybersecurity strategy

Shortage of IT support

The three cybersecurity priorities for 2021

The 7 main conclusions of the survey
Smaller businesses often think – wrongly – that their data or business is not sufficiently interesting to cybercriminals. SMEs have just as interesting and sensitive data, such as information on customers or companies, intellectual property rights, etc. These data are first and foremost of vital importance to the business itself.
And a data leak or cyber attack is all it takes to damage the relationship of trust with customers, partners or suppliers.
From our 2019 survey it appears that 19% of SMEs (the Netherlands: mkb) were the victim of a cyber incident.
That figure rose in 2020 by 23%, meaning that 42% were the victim of a cyber incident.
*An SME is a company with less than 250 employees. Companies of <100 and 100 - 250 employees fit within this category.


Every organization – big or small – is a potential target
12%
of the businesses surveyed don’t know whether or not they went without incident.
86%
of the businesses with more than 2,000 employees did encounter one or more incidents.
Conclusion
57%
of the businesses with fewer than 100 personnel stated that they had not experienced an incident.
54%
34%
12%

54% experienced an incident

34% experienced no incident

12% don’t know

By this we mean any malicious event or action that threatens the reliability, integrity and/or availability of the information systems of a business (the receipt of phishing e-mail, data breaches, unauthorized access, etc. with or without consequences or damage).
1 in 2 respondents were confronted with a cyber incident in 2020.*
Cyber incidents in small-to-large businesses
don’t know

had an incident

had no incident

< 100
employees
250 – 2.000
employees
> 2.000
employees
100 – 250 employees
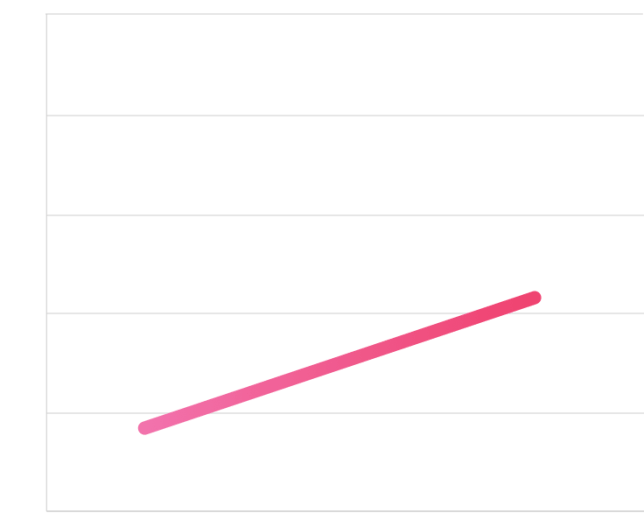
19%
42%


Phishing is the most common attack
2 out of 3 businesses fall victim to at least 1 internal incident every year.
How many facets does an insider threat have and how do you protect yourself from one?
Insider threat
During the lockdown hackers launched 19% more phishing attacks than ever before. They tried to profit from poorly secured home workstations to steal data or spread malware.
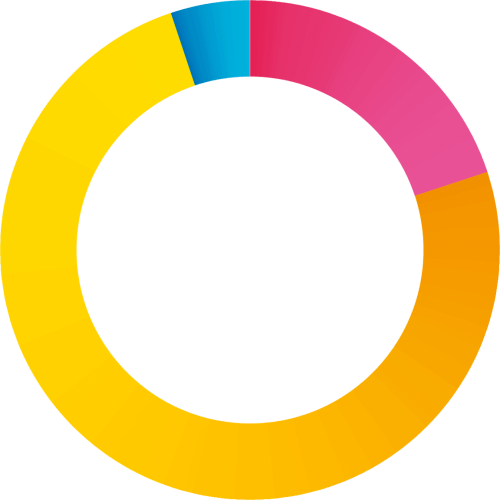
75%
20%
5%
75% External

20% Internal (insider threat)

5% I don’t know

75% of the attacks come from outside the business
3 out of 4 respondents had experienced an incident that came from outside the business, while 1 in 5 was confronted with insider threats.
Top 3 cyber incidents in 2020
1. Phishing: 35%
2. Malware: 16%, of which 52% were a virus and 33% ransomware
3. Spear-phising: 16%


An incident is not always visible
For 7 out of 10 respondents, the incident was discovered internally, while 15% were alerted by a third party. An incident cannot always be identified instantly. It demands continuous monitoring and system analysis.
Discovered internally: 69%

Flagged up by third party: 16%

I don’t know: 2%

Other: 13%

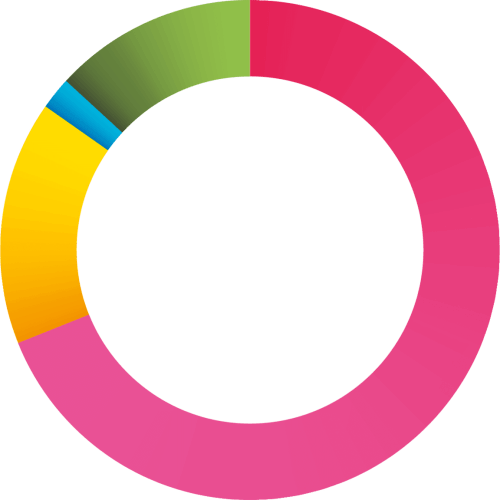
16%
69%
13%
2%
Take note: 92% of the businesses that had already experienced a cyber incident are concerned to very concerned about being a victim a second time. Of those businesses that hadn’t yet been attacked, 18% indicated not being concerned at all.

The consequences of an incident are often severe

Fortunately, in 85% of the incidents no data was lost. However, this was the case in 4% of the incidents. Remarkably – and worryingly – 11% of the affected businesses do not know whether or not they lost data.
loss of business data
In 9% of cases the incident was such that employees could no longer work.
technical unemployment
After an incident, 94% of businesses had the situation under control again within 4 weeks.
Nonetheless, 1 in 20 businesses didn’t have the situation under control after 6 months, which definitely has a huge impact on an organization. In a study by insurance broker Van Breda, in 38% of cases a cyber attack led to a network disruption or business stoppage.
business standstill
actual cost
According to insurance provider Hiscox, Belgian businesses wrongly estimate the costs of cyber incidents. According to businesses, one hacking incident costs 9,000 euros, while in reality that sum can rise to an average of 136,000 euros. A small Belgian manufacturing business with about 500,000 euro annual turnover sometimes loses up to 133,000 as a result of a cyber attack. It is mainly the stoppage of IT followed by planning and production that costs this kind of business handfuls of money.
In our survey many respondents found it difficult to express the costs linked to an incident in terms of percentage of annual turnover. Incidents were discovered in time, so there were no financial consequences for some. While others were faced with the cost of shutting down vulnerabilities and making employees extra aware of cyberthreats.

2%
2%
77%
15%
2%
2%
Time out period elapsed before situation was back under control:
Less than a week: 77%

Between 1 and 4 weeks: 15%

Between 3 and 6 months: 2%

Longer than 6 months: 2%

The problem is still not resolved: 2%

I don’t know: 2%



50% of the organizations have no active cybersecurity strategy
1 in 2 businesses in Belgium and the Netherlands has no active cybersecurity strategy or doesn’t know if they have one.
What is zero-trust security?
For a long time, IT security was focused exclusively on keeping the bad guys out. ‘Zero-trust’ changes that mindset. The assumption is that nothing can be trusted. Instead of banning things that are not allowed, zero-trust focuses on what is allowed.
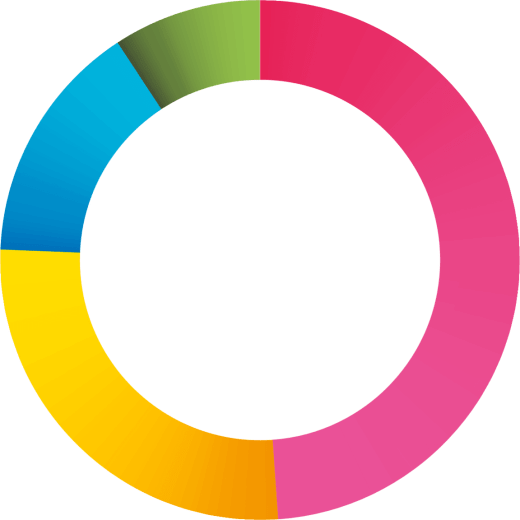
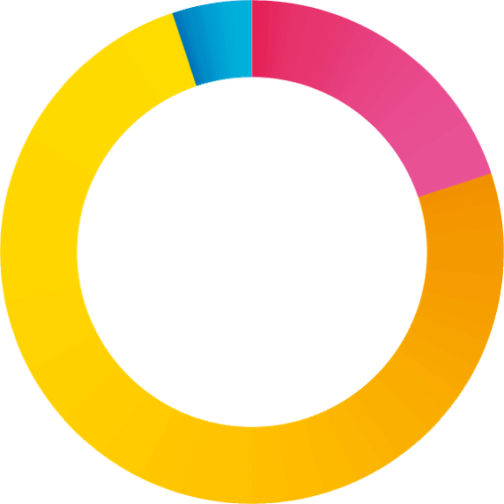
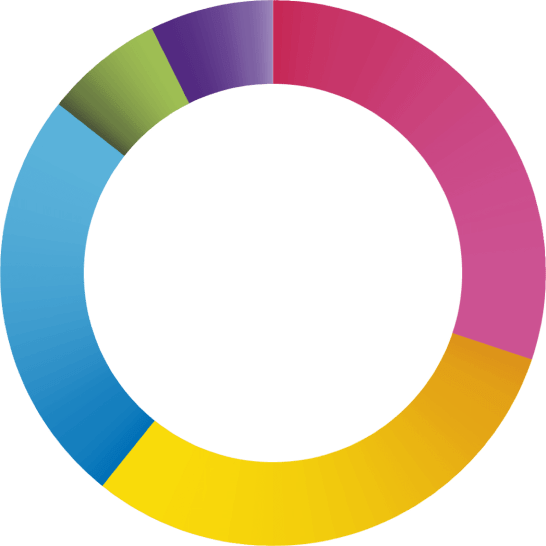
27%
49%
9%
15%
1. Information security
2. Threat prevention
3. Compliance with regulations
3 major motivations for the implementation of cybersecurity measures
3 major obstacles to the implementation of cybersecurity measures
Cybersecurity is a huge cost for businesses and is rarely if ever included in the budget. In many organizations there is still the perception that cybersecurity means huge costs and little to no ROI.
1. Financial
2. Business culture
If a strategy is not supported by management, then employees are not aware of the importance of cybersecurity and no one cares about it.
The IT environment – often in small businesses – is barely or never monitored. Lack of knowledge, capacity and/or personnel is the cause of this.
3. Resources
Almost 4 in 10 respondents admit to having a shortage of specialist people in the IT department. Of those businesses with more than 2,000 employees, 43% reported a shortage of cybersecurity employees.
22% of respondents said they had no cybersecurity employees at all. Of the businesses with fewer than 100 employees, 40% had no cybersecurity team.

3%
54%
39%
4%
Number of cybersecurity employees in the IT department
Who manages and monitors the cybersecurity infrastructure?

Shortage of IT support



Cybersecurity priorities for 2021
The study shows that many businesses are still suffering from a shortage of IT support. In addition, there are also businesses that have no strategy or are still developing one. 1 in 4 businesses do not give cybersecurity awareness training to their employees.
Our respondents know that they can and ought to do better. The three top cybersecurity priorities for 2021 are:
raising awareness among and training of employees
investing in technology
developing a cybersecurity strategy
1.
2.
3.

30%
31%
6%
7%
26%
Organizing small activities a few times a year, like a poster campaign or a stand in a central space in the building, can have a much bigger impact. Cybercrime is evolving at breakneck speed, which is why it is important to devote constant attention to the training of your personnel. With (online) mini-training sessions, your employees will constantly be aware of your business security approach.
Secure your business in 4 easy steps
Discover the Proximus 360°approach to making your organization secure. Pick and choose what you want: from total outsourcing to specific cybersecurity services.
The 13 cybersecurity trends and risks of 2021
The cybersecurity landscape is a constantly moving picture. It is best to prepare your organization for protecting new technologies and possible cyber incidents.